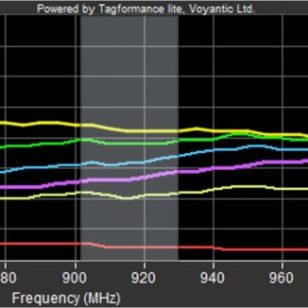
TIPP Grading (Tagged-Item Performance Protocol) is our most requested service, as it is based on the TIPP standard developed by GS1, which allows any retailer, supplier or system integrator, to choose the right tag for a given item and use case.
Why TIPP?
The TIPP Guideline is a set of documents that outline and explain the tagged item grading methodology, test configuration and grade definition, for specifying and verifying tagged item performance between trading partners (typically retailer and supplier).
The guideline allows retailers the flexibility to set performance levels for their use case and suppliers the flexibility in how they meet grade levels from multiple retailers.
The guideline allows retailers the flexibility to set performance levels for their use case and suppliers the flexibility in how they meet grade levels from multiple retailers.

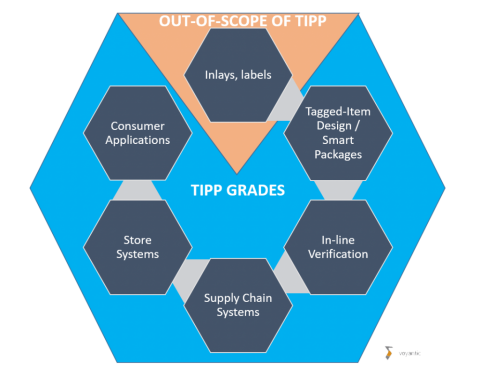
TIPP Grades
TIPP grades are named with a multi-dimensional naming system:
• “S” stands for single item, “M” stands for multiple items.
• The numbers (05, 10, 15, 20, etc…) specify item factor performance levels (higher numbers indicate higher performance).
• Letters “B”, “D”, and “V” specify the family to which the grade belongs.
• “S” stands for single item, “M” stands for multiple items.
• The numbers (05, 10, 15, 20, etc…) specify item factor performance levels (higher numbers indicate higher performance).
• Letters “B”, “D”, and “V” specify the family to which the grade belongs.
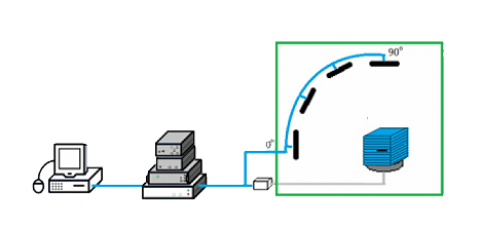
A TIPP grade contains the relevant performance factors for a RFID tagged-item operating in a retail environment:
• Orientation: The position of the interrogator antenna relative to the tagged-item.
• Sensitivity: the minimum power required for the tagged-item to respond to an RFID interrogator.
• Backscatter Power: the effective power level of the tagged-items response.
Each grade is defined by a set of tables that specify the tagged-item sensitivity and backscatter at various orientations.
• Orientation: The position of the interrogator antenna relative to the tagged-item.
• Sensitivity: the minimum power required for the tagged-item to respond to an RFID interrogator.
• Backscatter Power: the effective power level of the tagged-items response.
Each grade is defined by a set of tables that specify the tagged-item sensitivity and backscatter at various orientations.



In order to compare the results from the TIPP tests, not only the methodology must be strictly followed, but also a specific test equipment is required to produce accurate, consistent, and repeatable radio frequency (RF) measurements.
A unique ERT Code, generated for each test, certifies that the results on your report have been obtained with both the required methodology and equipment, thus authenticating the performed tests for you, your customers and partners.
A unique ERT Code, generated for each test, certifies that the results on your report have been obtained with both the required methodology and equipment, thus authenticating the performed tests for you, your customers and partners.

- RAIN RFID